In this guide, I’m going to introduce you to some of the optimizations you can make to your website, that tend to correlate with better performing websites and organic promotion campaigns.
This guide is for you if your website:
- Sells products directly to users (B2C e-commerce)
- Sells products to other businesses and manufacturers (B2B e-commerce)
- You sell a SaaS or FaaS product, such as a CDN or project management tool
- You sell holidays or non-tangible, similar travel products
As with all SEO lists, this isn’t exhaustive and there will be a lot of nuances and individual factors for specific keywords and verticals that will still need accommodating as part of your wider Yandex SEO strategy.
There are four elements that Yandex has highlighted in previously published documents that are taken into account when the search engine ranks commercial websites for commercial intent queries.
These are:
- The credibility of the website and association company
- Product depth and available information
- Price visibility
- Payment methods, delivery methods, and payment security
These four factors were outlined as part of an algorithm update in November 2011, and then later in 2013 in a co-authored paper, messers Alexander Shishkin, Polina Zhinalieva, and Kirill Nikolaev outlined a “commercial relevance scale”.
In contrast to searching for a single correct answer, such requests involve a number of possible answers to choose from. These groups of user requests include, in particular, commercial queries, where customers often want to choose the best offer between many similar ones.
The document also outlines a number of other interesting pointers, which 7 years on still ring true (from experience).


Commercial Relevance Scale
Yandex’s research defines early on that a document (a webpage) that is topically relevant for a commercial query possesses commercial relevance.
The quality of a document upon a commercial query provided that the document is topically relevant is called commercial relevance.
In this document, Yandex’s researchers essentially acknowledge a special focus on commercial intent query satisfaction versus non-commercial query satisfaction, and also acknowledged at the time that both user click-through data and human assessment data is/was used to ascertain SERP quality.
We know that Yandex uses Toloka members to help assess SERP quality and help train AI algorithms, as was disclosed last year during the Vega update announcement:
“People, or “assessors,” have long helped train our machine learning platforms through our crowdsourcing platform, Yandex.Toloka.
Using our search result evaluation guidelines, the assessors in Yandex.Toloka complete tasks that help us find the most relevant results for specific queries.”
We don’t, however, know what these raters look for specifically, as the Yandex equivalent of Google’s QRG hasn’t been disclosed to the public (well at least at the time of writing this, and trust me, I’ve asked them for it – and they don’t want to disclose it).
This paper however set about proposing a new model of how commercial relevance is judged algorithmically by “the creation of new facets of relevance and implementation of features, capturing the quality of a webpage” and that “on the basis of several quality facets, we form a cumulative rating, which is called commercial relevance“.
Aka, a series of markers that if scored positively for can determine that a page scores highly on a commercial relevancy scale for relevant queries.
The document also outlines a list kindly titled Features for measuring site quality, which contains:
- Detailed contact information
- Company’s pages in social networks
- Absence of advertising
- Number of different product items
- The verbosity of products description
- Availability of shipping service
- Salesclerk service (email, phone, customer feedback)
- Online consulting system
- Price discounts
- Readability of domain name
- Average URL length
- Average page title length
- Consistency of page title and page content
- The average depth of the URL path
And whilst this list is 7 years old, and I’m definitely not advocating that a live chat system (online consulting system) will improve your rankings, it does show that a large number of user “friendliness” factors were present in early thinking, and this has been continued through to 2020.
One final note on this document, Yandex’s researchers do acknowledge the commercial viability of ranking in traffic driving positions for commercial intent queries:
Commercial queries form highly competitive environment where position rise in search results means growth of site’s incomes. Thus, in order to increase profits commercial web sites do their best to take the place in the top of search results. Webmasters optimize textual content and buy incoming links to make it easier for a search engine to find their sites and present them to the users in response to the commercial queries. As a result, in terms of textual relevance and link-based quality measures, commercial sites in the top-10 are often equally relevant.
So it’s not all just focused on the users, but also understanding of why the world (and businesses) want to rank.
So how does the above list, and experience, dictate the four aforementioned factors:
Establishing The Credibility Of The Website And Associated Company
This is quite qualitative but is something that Yandex has the ability to apply a consistent scoring mechanism too. We know this from the fact websites can earn quality marks in the form of badges within search results.
And from the list outlined in the research paper, credibility can also be established through transparency and “wider signals”.
For example, detailed contact information can include:
- Telephone number (a local telephone number does have more “weight” than a mobile number)
- You can also use an 8-800 number if your site caters for users in multiple regions
- Email address
- Skype/Viber/Telegram
- Social media, e.g. Vkontakte
- Contact form
- Support hours
- Office/store locations
For the B2B sector, data, correlation, and superstition also dictate that information such as the tax ID, registered business address, and other legal registration information is a credibility factor. It’s also relatively important to have a verified listing in either Yandex.Direct or Yandex.Catalog, or both.
Other best practices that correlate with performance (and superstition now dictates it’s better to do these than not):
- Making sure your contact information is widely accessible from all pages on the website, e.g. a footer link
- Having a prominent phone number or email during support hours, e.g. a phone number in the header
Those two might sound like a given, but, you know, sometimes for design and sleekness basic user needs are forgotten.
This is also where the presence of an online consultant, aka live chat, could potentially be a factor. Non-intrusive live chat can be a blessing and an essential customer service tool, so the logic makes sense as to why the presence of one can be helpful.
Good Product Pages And Information
In this section, I’m combining two of the four factors I outlined in the introduction, and breaking this section down further into 3 areas:
- Product listing page information & design
- Product listing page maintenance and stock control
- Product range and supporting products
- Clear delivery methods and instructions
- Clear payment methods (that are secure)
This is where SEO also needs to “get involved” in other decisions and channels, as regardless of the function within the e-commerce business, the objective is the same – all the cogs turn in the machine to sell more stuff and make more money.
So when it comes down to the above, it’s relatively self-explanatory, but who is doing this well? In my opinion, Ozon. Let’s take a look at their product page template for tomatoes.
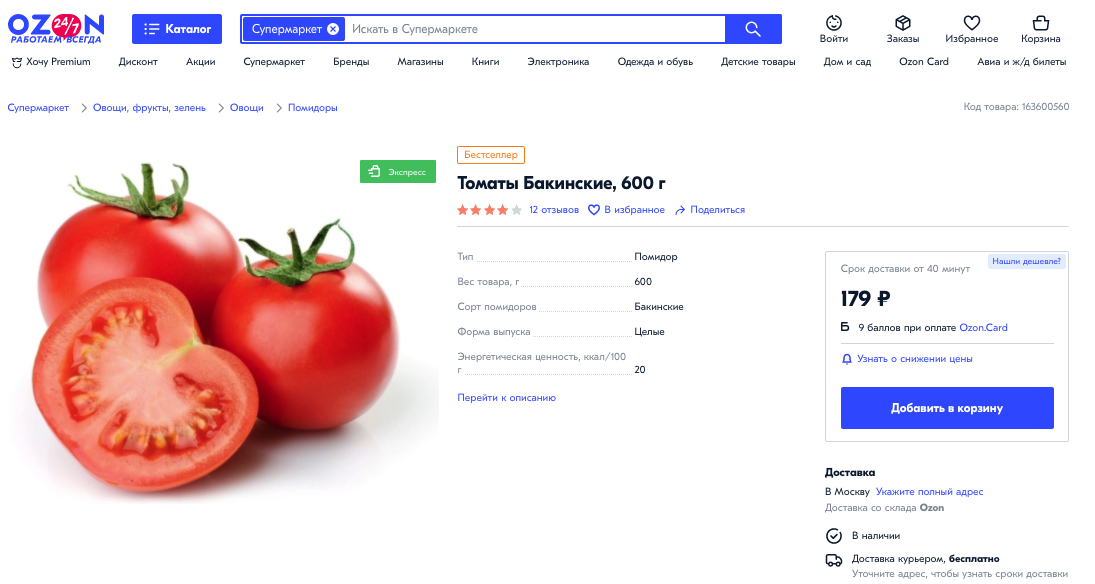

When a user lands on the page, there is a clear user-friendly breadcrumb, an express checkout option in a nice green CTA, the product title and weight, the variety of tomato (Baku, for those who were curious), the cost, a price match feature (Нашли дешевле?), price drop alerts, and add to cart.
Underneath the blue add to cart button is a section outlining delivery and courier options, as well as reassurance that “We deliver products in thermal containers to preserve their fresh taste.”
The page also contains:
- Customer photos (Фотографии покупателей)
- Secure payment information
- “Also bought together” section (which contained other tomatoes and bananas)
- “Recommended products” section
- “Bought with this product” a section differing to also bought together (see below)
- A concise but comprehensive product description (all about the Baku tomatoes)
- Links to other tomato products (and varieties)
- Customer reviews of the product
The “Also bought together” section contains two products that are frequently checked out by users and allows for a quick “add to cart” of all the items. The Bought with this product section contains a wider variety of fruit and vegetables, and whilst they are often bought alongside the items in the other section, the frequency is less.
This great UI encompasses a number of the relevance factors detailed previously, these being:
- Absence of advertising
- Number of different product items
- The verbosity of products description (or lack of verbosity)*
- Availability of shipping service
- Salesclerk service (email, phone, customer feedback)
- Price discounts
- Consistency of page title and page content
* This also helps put to rest the notion that comprehensive content needs to be longer in length and verbose.
Integration With Wider Systems
This seamless product page is also a triumph of integrations with backend systems that aren’t (by standard) in the realms of SEO, but making sure that the website can reflect when a product is out of stock or there are delivery issues can lead to positive user experiences with the brand.
It also allows for interaction and further engagement with the user, e.g. “notify me when back in stock” email gauntlets, thus supporting other channels.
This is why when scoping the technical capabilities of a website, there are theoretical grounds that having these capabilities on the website will yield SEO benefits, especially if the competition has the functionalities in place.







